As evidenced by the COVID-19 pandemic, we are facing new social, economic, and environmental challenges. We need to generate ways to advance towards a green recovery, achieve the objectives of the 2030 Agenda and ensure we can quickly respond to new challenges and crises. Technology and innovation can be powerful enablers of this adaptation.
UNDP has created a unique framework to understand how cities can innovate leveraging their existing resources embodying a set of features that can be used to characterize smart and sustainable cities, focusing on innovative approaches that contribute to solving concrete urban challenges.
This approach is based on the concept of “smart urban innovations”. These are concrete initiatives or projects that provide solutions to challenges faced by the needs of a city’s residents. These solutions mobilize the actors of the local innovation ecosystem and different sets of resources to solve concrete challenges in all sectors where cities operate.
The Urban Innovations Wheel framework highlights the most common combination of elements, and allows us to generate a typology of urban innovations.
Starting at the centre of the circle and moving towards its outer edge, the Urban Innovation Wheel encompasses four dimensions that we find in all Smart Urban Innovations and presents a set of possibilities for each.

Each type of Smart Urban Innovation results from the interplay of four different components: actors, their roles, data and information, and broader tools. In each type of Smart Urban Innovation, we see the mobilization of one or more aspects of each component.
The interplay of possibilities associated with each dimension of the wheel creates distinct patterns and leads to the identification of four discrete types of Smart Urban Innovations.
Frugal InnovationsMarket-driven, frugal solutions stemming from the community, with government or private sector acting as enablers. 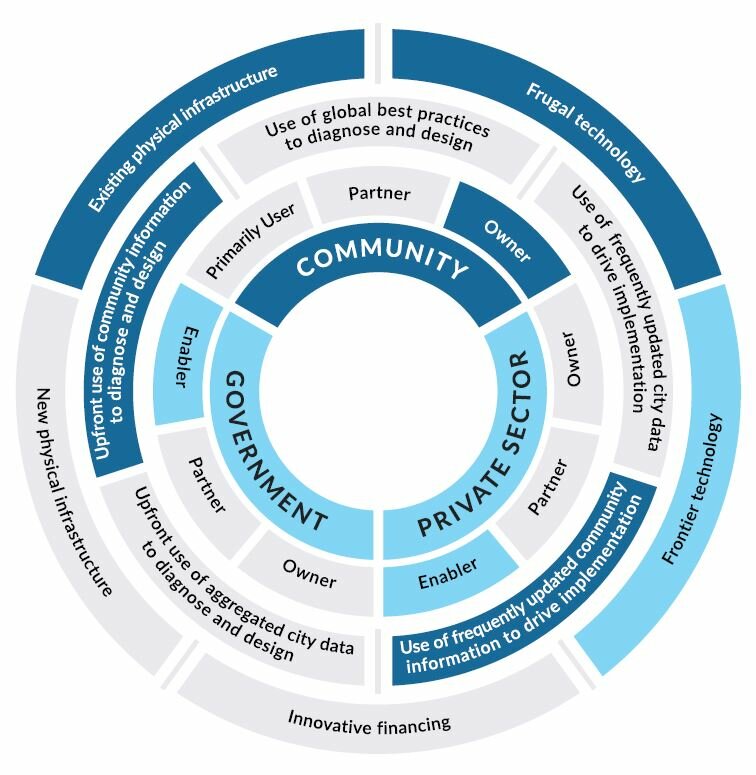
|
Community OrganisedCommunity-led, locally-inspired and resourceful solutions driven by civil society, with direct support from the government or private sector. 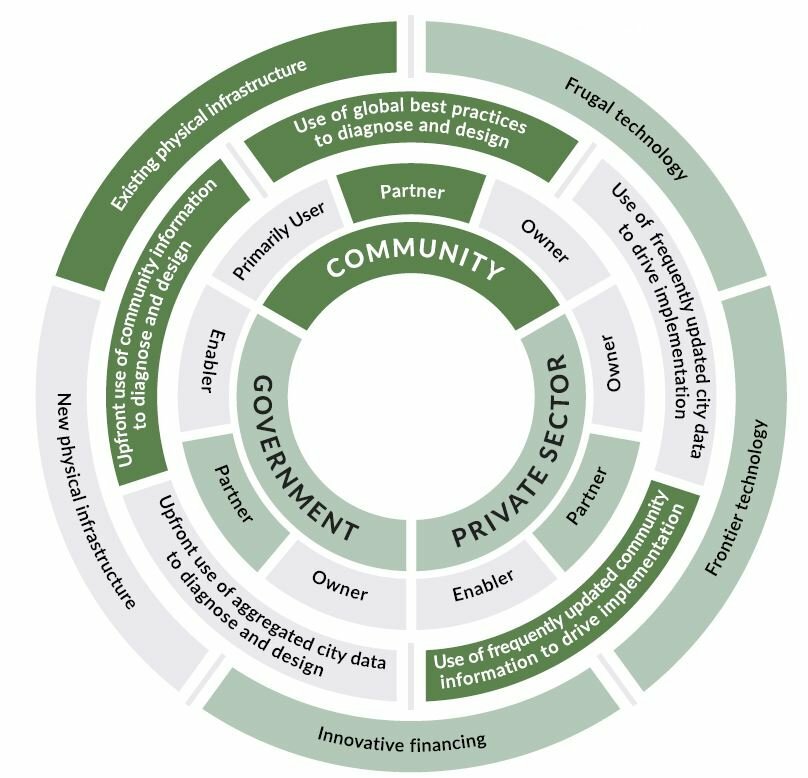
|
Enterprise VenturersPrivate-sector led, technology-centric and dynamic solutions, with governments creating the right conditions for success. 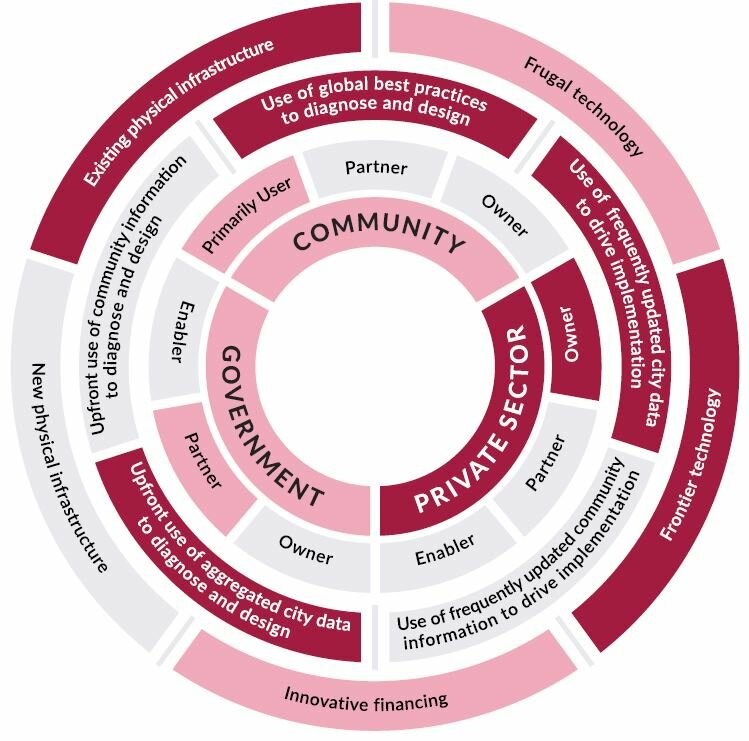
|
Institutional PioneersGovernment-led, city-wide solutions that are catalytic and anchored on the use of significant state resources, often in partnership with the private sector. 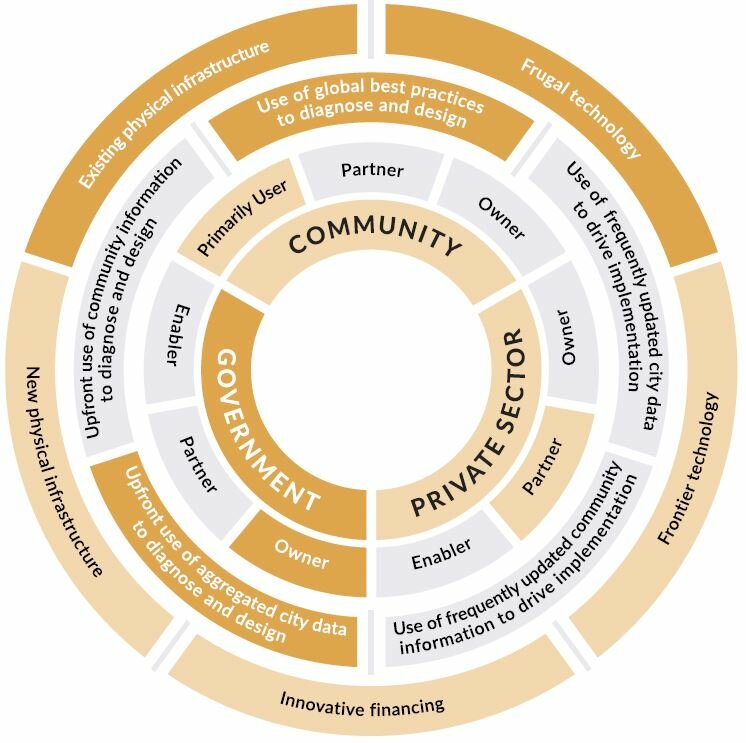
|








